Cybersecurity Protocols: Reduce US Breach Risk by 20% by Q2 2025

Implementing advanced cybersecurity protocols across US enterprises by Q2 2025 is crucial for achieving a 20% reduction in breach risk, necessitating strategic planning and continuous adaptation to evolving threats.
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, the imperative for robust security has never been greater, especially for US enterprises. This guide outlines practical solutions: implementing advanced cybersecurity protocols for US enterprises by Q2 2025 – a step-by-step guide to reducing breach risk by 20%. Navigating the complexities of modern cyber threats requires a strategic, forward-thinking approach that goes beyond basic defenses.
Understanding the Evolving Threat Landscape
Before diving into solutions, it is crucial to grasp the current state of cyber threats. Attacks are becoming more sophisticated, targeting not just financial data but also intellectual property, operational technology, and critical infrastructure. US enterprises face a unique set of challenges, including state-sponsored attacks and insider threats, making a static defense strategy obsolete.
The sheer volume and variety of threats necessitate a dynamic and adaptable cybersecurity posture. Cybercriminals constantly innovate, exploiting new vulnerabilities and employing advanced tactics like AI-driven phishing and polymorphic malware. Organizations must anticipate these changes, shifting from reactive defense to proactive threat intelligence and prevention.
The Rise of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs represent a significant danger, characterized by their stealth and persistence. These attacks often involve:
- Long-term infiltration to exfiltrate sensitive data.
- Sophisticated evasion techniques to bypass traditional security.
- Targeted social engineering to gain initial access.
Understanding the modus operandi of APTs is the first step in building a resilient defense. This requires not just technical controls but also a culture of security awareness across the entire organization.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Another critical area of concern is the supply chain. A single weak link in a vendor’s security can compromise an entire enterprise. This means:
- Thorough vetting of third-party vendors’ security practices.
- Implementing strict access controls for vendor integrations.
- Continuous monitoring of supply chain risk.
Enterprises must extend their security perimeter beyond their immediate infrastructure to encompass all entities that interact with their systems and data. This holistic view is essential for a comprehensive risk reduction strategy.
In conclusion, the threat landscape is dynamic and multifaceted. US enterprises must move beyond conventional security measures to embrace a more adaptive and intelligent defense strategy. This involves a deep understanding of current and emerging threats, coupled with a commitment to continuous improvement in security posture.
Establishing a Robust Cybersecurity Framework
To effectively reduce breach risk, US enterprises need a well-defined and robust cybersecurity framework. This framework serves as the backbone for all security initiatives, providing structure and guidance. It should align with industry best practices and regulatory requirements, ensuring comprehensive coverage and compliance.
A strong framework helps organizations identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover from cyber incidents. It is not a one-time implementation but an ongoing process that evolves with the business and the threat landscape. The goal is to create a resilient environment where security is integrated into every aspect of operations.
Adopting the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework is widely recognized and provides a flexible approach to managing cybersecurity risk. Its core functions include:
- Identify: Understanding your assets, systems, capabilities, and potential risks.
- Protect: Implementing safeguards to ensure delivery of critical services.
- Detect: Developing capabilities to identify cybersecurity events.
- Respond: Taking action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident.
- Recover: Planning for resilience and restoring capabilities.
Implementing the NIST framework provides a structured approach to assessing and improving cybersecurity posture. It allows organizations to prioritize investments and allocate resources effectively, focusing on areas of highest risk.
ISO 27001 Certification
For enterprises seeking international recognition and a more rigorous approach, ISO 27001 certification is invaluable. This standard specifies requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS). Key benefits include:
- Enhanced credibility and trust with customers and partners.
- Systematic management of information security risks.
- Compliance with various legal and regulatory requirements.
Achieving ISO 27001 demonstrates a commitment to information security at the highest level, providing a competitive advantage and a solid foundation for risk reduction efforts. It involves a detailed audit process, ensuring that security controls are not just in place but are also effective and continuously reviewed.
Building a robust cybersecurity framework is foundational to any successful risk reduction strategy. By adopting established frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001, US enterprises can create a structured, comprehensive, and continuously improving security program, moving closer to their Q2 2025 breach risk reduction goals.
Implementing Advanced Threat Detection and Prevention
Effective cybersecurity goes beyond basic firewalls and antivirus software. Advanced threat detection and prevention mechanisms are vital for identifying and neutralizing sophisticated attacks before they cause significant damage. These solutions leverage cutting-edge technologies to provide real-time insights and proactive defense capabilities.
The focus should be on creating a multi-layered defense that can detect anomalies, analyze behavior, and respond swiftly. This involves integrating various tools and strategies that work in concert to provide comprehensive protection across the entire IT ecosystem. Early detection is often the key to minimizing the impact of a cyberattack.
Next-Generation Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Traditional endpoint protection struggles against fileless malware and zero-day exploits. EDR solutions offer superior capabilities by:
- Continuously monitoring endpoint activity for suspicious behavior.
- Providing deep visibility into security incidents.
- Automating threat response and remediation.
Deploying EDR across all endpoints, including servers, workstations, and mobile devices, creates a powerful defense layer. It allows security teams to quickly identify and contain threats, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers. Behavioral analysis is a core component, distinguishing legitimate activity from malicious intent.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) with SOAR
SIEM systems aggregate and analyze security logs from various sources, providing a centralized view of an organization’s security posture. Integrating SIEM with Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) capabilities further enhances its effectiveness:
- Automation: Automating routine security tasks and threat responses.
- Orchestration: Coordinating disparate security tools and workflows.
- Response: Streamlining incident response processes.
This combination allows security teams to manage alerts more efficiently, reduce manual effort, and respond to threats at machine speed. It transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, enabling faster and more informed decision-making during a security incident. The ability to correlate events across the entire network provides unparalleled insight into potential attacks.
Implementing advanced threat detection and prevention tools is non-negotiable for US enterprises aiming to reduce breach risk by Q2 2025. By leveraging EDR, SIEM, and SOAR, organizations can establish a proactive defense that identifies and mitigates threats before they escalate, safeguarding critical assets and maintaining operational continuity.
Strengthening Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a cornerstone of any robust cybersecurity strategy. It ensures that only authorized individuals and entities have access to sensitive systems and data, thereby significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access and insider threats. Poor IAM practices are often exploited in data breaches, making its reinforcement a high priority.
Effective IAM involves more than just passwords; it encompasses a suite of technologies and policies designed to manage digital identities and control access to resources. The goal is to provide the right access to the right people, at the right time, for the right reasons, and to continuously monitor that access.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Everywhere
MFA adds a critical layer of security beyond traditional passwords by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access. This can include:
- Something they know (password).
- Something they have (phone, hardware token).
- Something they are (biometrics).
Implementing MFA across all critical systems, applications, and VPNs dramatically reduces the risk of credential theft and phishing attacks. Even if a password is compromised, the attacker still needs the second factor, significantly increasing the difficulty of unauthorized access. It should be considered standard practice for all enterprise users.
Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
The Principle of Least Privilege dictates that users and processes should be granted only the minimum necessary access rights required to perform their job functions. This practice minimizes the potential damage from compromised accounts or insider threats by:
- Limiting the scope of what an attacker can access.
- Reducing the attack surface for internal systems.
- Enhancing accountability for user actions.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting access permissions is crucial to maintain PoLP, especially as roles and responsibilities change within an organization. Automated tools can assist in identifying and remediating excessive privileges, ensuring that access remains aligned with operational needs and security best practices.
Strengthening IAM through widespread MFA implementation and adherence to the Principle of Least Privilege is fundamental for US enterprises aiming for a 20% breach risk reduction by Q2 2025. These practices create a more secure environment by tightly controlling who can access what, thereby mitigating a significant portion of common cyber risks.
Developing a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
Even with the most advanced prevention measures, incidents can occur. A well-developed and regularly tested incident response plan is critical for minimizing the damage and recovery time after a cyberattack. This plan provides a structured approach to detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents, ensuring business continuity.
An effective incident response plan is not just a document; it is a living process that involves people, technology, and procedures working in harmony. It must be clear, actionable, and understood by all relevant stakeholders within the organization. The speed and efficiency of response can often dictate the overall impact of a breach.
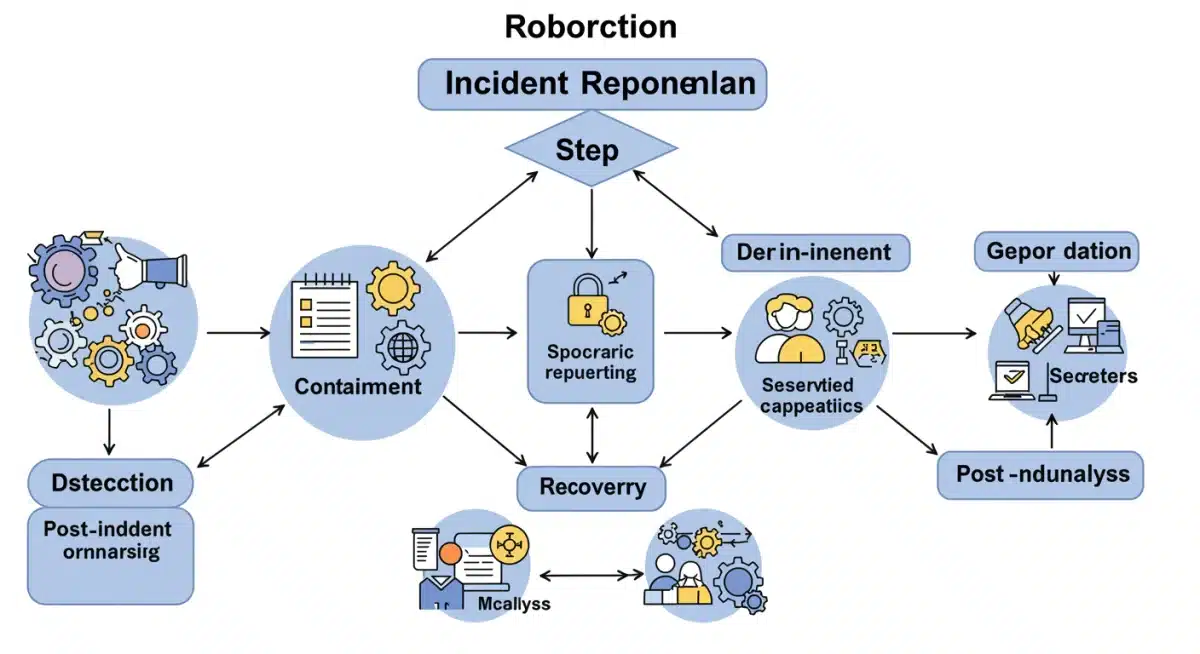
Key Phases of Incident Response
A comprehensive incident response plan typically includes several key phases:
- Preparation: Establishing policies, procedures, and teams before an incident occurs.
- Detection & Analysis: Identifying and thoroughly understanding the scope and nature of the incident.
- Containment: Limiting the damage and preventing further spread of the attack.
- Eradication: Removing the root cause of the incident and any malicious elements.
- Recovery: Restoring affected systems and data to normal operations.
- Post-Incident Activity: Learning from the incident to improve future security.
Each phase requires specific actions and clear communication protocols. Regular training and drills are essential to ensure the incident response team is prepared to execute the plan effectively under pressure. This proactive preparation reduces chaos during a real event.
Communication Strategy and Legal Compliance
During a security incident, effective communication is paramount, both internally and externally. The plan should outline:
- Who needs to be informed and when (e.g., legal, PR, board members).
- How to communicate with affected parties (customers, regulators).
- Compliance requirements for data breach notification laws (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, state-specific laws).
Legal counsel should be involved early in the planning process to ensure all communications and actions comply with applicable regulations. Transparency, where appropriate, can help maintain trust with customers and stakeholders, even in the event of a breach. A well-managed communication strategy can mitigate reputational damage.
A robust incident response plan is a non-negotiable component of reducing breach risk. By meticulously preparing for potential incidents, US enterprises can ensure a swift, organized, and effective response, minimizing the impact of attacks and accelerating recovery, thereby safeguarding their journey towards a 20% breach risk reduction by Q2 2025.
Cultivating a Security-Aware Culture
Technology alone cannot secure an enterprise; human factors play a critical role in cybersecurity. A strong security-aware culture empowers every employee to be a part of the defense mechanism, turning them from potential vulnerabilities into active protectors. This cultural shift requires ongoing education, clear policies, and visible leadership commitment.
Human error remains a leading cause of data breaches. Therefore, investing in people is just as important as investing in technology. When employees understand the risks and their role in mitigating them, the overall security posture of the organization is significantly enhanced. It’s about making security a shared responsibility.
Ongoing Security Awareness Training
Regular and engaging security awareness training is essential. It should cover a range of topics, including:
- Phishing and social engineering recognition.
- Password best practices and MFA usage.
- Safe browsing habits and data handling procedures.
- Reporting suspicious activities.
Training should not be a one-off event but a continuous program that adapts to new threats and technologies. Interactive modules, simulated phishing exercises, and real-world examples can make training more effective and memorable. The goal is to instil a habit of security-conscious behavior among all employees, from the mailroom to the boardroom.
Leadership Buy-in and Policy Enforcement
For a security-aware culture to thrive, it must be championed by leadership. When senior management visibly prioritizes cybersecurity, it sends a clear message throughout the organization. This includes:
- Allocating sufficient resources to security initiatives.
- Enforcing clear and consistent security policies.
- Leading by example in adhering to security best practices.
Policies should be easily accessible, understandable, and regularly reviewed to ensure their relevance. Consequences for non-compliance, alongside recognition for adherence, reinforce the importance of security protocols. A top-down commitment ensures that security is not seen as merely an IT issue but as a fundamental business imperative.
Cultivating a robust security-aware culture is indispensable for US enterprises aiming to reduce breach risk. By continuously educating employees and securing strong leadership buy-in, organizations can transform their workforce into a formidable line of defense, significantly contributing to the Q2 2025 goal of a 20% reduction in breach risk.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Cybersecurity is not a static state but an ongoing process. The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and so too must an enterprise’s defense mechanisms. Continuous monitoring and a commitment to ongoing improvement are vital to maintaining a strong security posture and achieving long-term risk reduction goals. This proactive approach ensures that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed before they can be exploited.
Regular assessments, audits, and penetration testing help identify weaknesses in existing controls and processes. The insights gained from these activities inform necessary adjustments and upgrades, ensuring that the cybersecurity protocols remain effective against emerging threats. It’s a cycle of vigilance and adaptation.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
To identify vulnerabilities, enterprises must regularly conduct:
- Security Audits: Comprehensive reviews of security policies, configurations, and controls.
- Vulnerability Assessments: Scanning systems for known security weaknesses.
- Penetration Testing (Pen Testing): Simulating real-world attacks to test the effectiveness of defenses.
These activities provide an external and objective perspective on an organization’s security strengths and weaknesses. Findings from audits and pen tests should be meticulously documented, prioritized, and addressed promptly. This iterative process ensures continuous hardening of the security perimeter and internal systems.
Threat Intelligence Integration and Adaptation
Integrating up-to-date threat intelligence into security operations is crucial for staying ahead of attackers. This involves:
- Subscribing to reputable threat intelligence feeds.
- Analyzing emerging attack vectors and tactics.
- Adjusting security controls and policies based on new intelligence.
By understanding what threats are on the horizon, enterprises can proactively strengthen their defenses. This predictive capability allows for the implementation of preventative measures rather than purely reactive ones. Staying informed about geopolitical events and technological advancements that could influence cyber threats is also part of this intelligence gathering.
In summary, continuous monitoring and improvement are non-negotiable for US enterprises committed to reducing breach risk by Q2 2025. Through regular audits, penetration testing, and the integration of dynamic threat intelligence, organizations can ensure their cybersecurity protocols remain robust, adaptable, and highly effective against an ever-changing threat landscape.
| Key Protocol | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| NIST Framework Adoption | Structured approach to identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover from cyber risks. |
| Advanced Threat Detection | Utilizing EDR and SIEM/SOAR for real-time monitoring and automated response. |
| Strong IAM & MFA | Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication and Least Privilege across all systems. |
| Incident Response Plan | Pre-defined steps for detection, containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident analysis. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Cybersecurity Protocols
▼
The primary goal is to significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks for US enterprises, specifically targeting a 20% reduction in breach risk by Q2 2025. This involves protecting sensitive data, ensuring operational continuity, and maintaining stakeholder trust through proactive and adaptive security measures.
▼
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is recommended for its flexible, risk-based approach to managing and improving cybersecurity. It provides a common language and systematic framework for organizations to identify, protect, detect, respond, and recover from cyber incidents, aligning with both industry best practices and regulatory needs.
▼
MFA significantly reduces breach risk by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification beyond just a password. This makes it much harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access, even if they manage to steal credentials through phishing or other methods, thereby fortifying access controls.
▼
Continuous monitoring is crucial because the cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving. It involves regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to identify and address weaknesses proactively. This ensures that security protocols remain effective and adaptable against new and emerging threats.
▼
A security-aware culture is vital because human error is a leading cause of breaches. Educated employees can recognize and report threats like phishing, follow secure practices, and understand their role in protecting sensitive data. This transforms them into an active defense layer, complementing technological safeguards.
Conclusion
Achieving a 20% reduction in breach risk for US enterprises by Q2 2025 is an ambitious yet attainable goal, provided a strategic and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity is adopted. This involves not only implementing advanced technical protocols but also fostering a pervasive security-aware culture and establishing robust incident response capabilities. By understanding the evolving threat landscape, adopting proven frameworks, leveraging cutting-edge detection tools, strengthening identity management, and committing to continuous improvement, enterprises can build formidable defenses. The journey towards enhanced cybersecurity is ongoing, requiring vigilance, adaptability, and an unwavering commitment to protecting digital assets. Proactive measures and a holistic strategy are the keys to safeguarding against future cyber threats and ensuring long-term resilience.